Loading... # 1.Google Test的介绍 ## 1.1 Why google test ``` google test helps you write better C++ tests. google test is a testing framework developed by the Testing Technology team with Google's specific requirements and constraints in mind. No matter whether you work on Linux, Windows, or a Mac. if you write C++ code, google test can help you. And it supports any kind of tests, not just unit tests.[^google test 在 GitHub的介绍^] ``` ## 1.2 google test case Test Case原意是指一个测试条件集合,这个条件集合定义了系统在此集合下的行为 一个简单的测试声明需要使用TEST宏。TEST宏有两个参数:测试用例的名称和测试的描述性名称。TEST(TestSuiteName, TestName) { ... test body ... } 根据Google的文档,测试用例是一些能共享数据的字程序的测试集合。从左到右阅读测试用例名称,可以连成一句话,描述了我们想要验证的行为。测试的描述性名称可以为开发人员快速提供一个有关代码行为的准确描述。测试的描述性名称越容易理解,开发人员能越快找到需要的东西。1.2.1 FALED TEST Google Mock给出的相关输出信息可能不太容易读懂。从最后一行开始看。如果是PASSEED,可以不用看测试的输出,因为所有测试都过了。如果是FAILED(正如示例一样),我们可以看到有多少测试失败了。如果是其他类别的信息,则是测试程序在一个测试运行过程中崩溃了如果有一个或多个测试失败了,可以从下至上观察Google Mock输出信息,找到失败的测试。Google Mock会在每个测试名称前输出一个[RUN],在测试失败的情况下输出[FAILED]或[OK]。失败的时候,[RUN]和[FAILED]之间的信息行可以帮助我们了解测试为什么失败 ```jsx #include <iostream> #include <gtest/gtest.h> using namespace std; TEST(Testdemo1, TestFailed) { ASSERT_TRUE( 1 == 2 ); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); } ``` 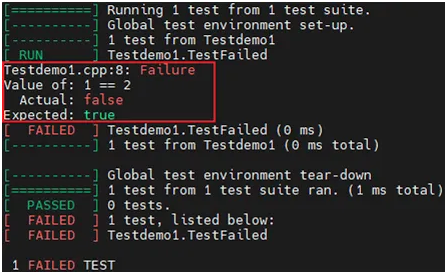 ## 1.3 Basic usage ### 1.3.1 Assertions: Fatal Failure : 致命错误 ASSERT\_TRUE or ASSERT\_FALSE or ASSERT\_EQ or ASSERT\_NE or ASSERT\_STREQ 出错之后的后面语句都不会被执行,一个test case里面可以出现一个assert或者多个assert Non-Fatal Failure : 非致命错误 EXPECT\_EQ EXPECT\_NE EXPECT\_STREQ出错之后的后面语句仍可被执行tips: googletest support EXPECT\_EQ(NULL, ptr) and ASSERT\_EQ(NULL, ptr) but not EXPECT\_NE(NULL, ptr) and ASSERT\_NE(NULL, ptr) # 2.Gmock的介绍 ## 2.1 fixture ``` fixture与设置Google Mock允许我们定义一个fixture类,我们可以在这个类中为相关的测试声明函数和数据从技术角度说,所有的Google Mock测试都使用一个由Google Mock自己生成的fixture。GMock会在运行每个测试时创建fixture类实例。在创建每个case之前,都会先创建一个类实例。为了使用自定义的fixture,我们把TEST宏替换为TEST_F,F表示fixture。如果忘记使用fixture,任何使用fixture类成员的测试代码都会编译失败。 ``` 常用用法(使用New,别使用Old) refer to: [http://google.github.io/googletest/gmock\_cook\_book.html](http://google.github.io/googletest/gmock_cook_book.html) | Simple | | | -------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- | | Old | `MOCK_METHOD1(Foo, bool(int))` | | New | `MOCK_METHOD(bool, Foo, (int))` | | Const Method | | | Old | `MOCK_CONST_METHOD1(Foo, bool(int))` | | New | `MOCK_METHOD(bool, Foo, (int), (const))` | | Method in a Class Template | | | Old | `MOCK_METHOD1_T(Foo, bool(int))` | | New | `MOCK_METHOD(bool, Foo, (int))` | | Const Method in a Class Template | | | Old | `MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_T(Foo, bool(int))` | | New | `MOCK_METHOD(bool, Foo, (int), (const))` | # 3.How to write UT > 单元测试包括一个描述性的名称和一系列代码声明,从概念上可以细分成四个(有序的)部分,我们也称之为: Arrange: Arrange everything required to run the Test(测试的初始化)---->Act: Run the test(测试的行为)----> Assert: Verify the output(怎样验证行为结果) > > * 设置能够运行上下文的语句,这一部分是可选的 > * 一条或多条能构成你想要验证的行为的语句; > * 一条或多条验证期望输出的语句 \*清理工作的语句(例如,释放所分配的内存,关闭之前打开的数据库连接),是这一部分是可选的 > 测试行为而非方法 > > * 不要把集中精力去测试成员函数。实现了一个add()成员函数,再写一个TEST(xxxx, Add)的测试。但是,写一个完全覆盖add的行为测试需要考虑多种不同的情形。结果必须将许多不同的行为进行编码进同一个测试,这样需要花费大量时间(所以不建议使用分支测试方法) > * 相反,应该把注意力集中在行为或描述行为的情形上。(建议使用语句测试方法) > * 可参考恒生官方单元测试培训 > 测试结构 > > * 文件组织 一致的命名约定可以让开发人员更容易找到需要的测试,一个xxx.cpp文件对应一个xxx\_unittest.cpp > * Fixture > > ``` > Test Fixtures: Using the Same Data Configuration for Multiple Tests {#same-data-multiple-tests} > When using a fixture, use TEST_F() instead of TEST() as it allows you to access objects and subroutines in the test fixture: > TEST_F(TestFixtureName, TestName) { > ... test body ... > } > Like TEST(), the first argument is the test suite name, but for TEST_F() this must be the name of the test fixture class. You've probably guessed: _F is for fixture. > > ``` > > * SetUp and Teardown > > ``` > Initializes it via SetUp(). > Cleans up the fixture via TearDown(). > > ``` > > * main > > ``` > int main(int argc, char **argv) { > ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); > return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); > } > The ::testing::InitGoogleTest() function parses the command line for googletest flags, and removes all recognized flags. This allows the user to control a test program’s behavior via various flags, which we’ll cover in the AdvancedGuide. You must call this function before calling RUN_ALL_TESTS(), or the flags won’t be properly initialized. > > when RUN_ALL_TESTS() is called, it first calls the SetUp() method of each environment object, then runs the tests if none of the environments reported fatal failures and GTEST_SKIP() was not called. RUN_ALL_TESTS() always calls TearDown() with each environment object, regardless of whether or not the tests were run. > > Note that RUN_ALL_TESTS() runs all tests in your link unit–they can be from different test suites, or even different source files. > > ``` > > Google官方也给了很多demo以及怎么写googletest [googletest samples.](https://github.com/google/googletest/tree/master/googletest/samples) # 4.How to debug UT 我们把执行一遍所有的测试称之为运行测试(test run或suite run)。在运行测试的过程中,工具会枚举所有的测试,独立地执行每个测试。对于每个测试来说,测试工具都是从头到尾执行其中的语句 > 4.1 disable掉test case 在GMock中,在测试用例名称前加上DISABLE\_前缀会跳过执行测试 > > 如果遇到不能很快fix的broken test,注释掉UT代码是可以的,但更好的办法是把测试标记为禁用,显示的警用测试的功能,并且在运行所有测试时提示哪些是被禁用的,在GMock中,在测试名称前加上DISABLE\_前缀来禁用测试 > > ``` > If you need to disable all tests in a test suite, you can either add DISABLED_ to the front of the name of each test, or alternatively add it to the front of the test suite name. > For example, > // Tests that Foo does Abc. > TEST(FooTest, DISABLED_DoesAbc) { ... } > class DISABLED_BarTest : public testing::Test { ... }; > // Tests that Bar does Xyz. > TEST_F(DISABLED_BarTest, DoesXyz) { ... } > > ``` > 4.2 跟踪测试数目有助于快速判断是否犯了以下错误 > > * 运行了错误的测试集 > * GMock过滤器忽略了新的测试 > * 测试并没有经过编译或链接 > * 测试被禁止了 > > 4.3 只运行一部分test case > > ``` > Running a Subset of the Tests > By default, a googletest program runs all tests the user has defined. Sometimes, you want to run only a subset of the tests (e.g. for debugging or quickly verifying a change). If you set the GTEST_FILTER environment variable or the --gtest_filter flag to a filter string, googletest will only run the tests whose full names (in the form of TestSuiteName.TestName) match the filter. > ./foo_test Has no flag, and thus runs all its tests. > ./foo_test --gtest_filter=FooTest.* Runs everything in test suite FooTest . > ./foo_test --gtest_filter=FooTest.TestName Runs TestName in test suite FooTest . > > ``` > 4.4 把结果打印信息输出到文本中 ./my\_test > gtest\_output.txt > 4.5 使用GDB调试 # 5.UT代码规范 > 总结一些测试中的不太好的使用: > > * 在写测试时,不要跑去重构。同样,在尝试让测试通过时,不要去重构。将两件事情一起做时,一旦出岔子会浪费时间。而且这肯定会发生 > * 它必须能够独立运行 而且它不依赖于任何外部输入 > * 一次只做一件事情,一个方法中有太多test case-被测试的方法做了太多事情 > * 改变一个地方,多处受影响--也许是测试的设计问题,也许是实现代码有过多依赖 > * 测试运行速度缓慢,表示当前单元测试也许在使用外部系统,例如网络、数据库、文件系统等。通常也意味着测试类有过多的职责 > 5.1 使用命名空间using EQ()所在的命名空间是一个与测试本意无关的实现细节。隐藏这一细节可以提升测试中的抽象程度 ASSERT(encode, testing::Eq("A")); using : testing: Eq ASSERT(encode, Eq("A")); ``` //标准库 #include <iostream> #include <vector> //第三方库 //#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp> #include <gtest/gtest.h> #include <gmock/gmock.h> //其他编译需要的.hpp文件 //UT namespace using ::testing::AtLeast; using ::testing::Return; using ::testing::_; using ::testing::Invoke; using ::testing::InvokeWithoutArgs; using namespace testing; //Src code namespace using namespace std; ``` > 5.2 不要提交在test case中加入额外调试的打印,如果要提交,请注释起来 > 5.3 让测试名称testname更容易理解 > > ``` > 概括了在特定上下文中系统表现出的行为,通过名字就能大概理解这个case的主要目的 should+result+if/when+action(if/when+action 有时可省略) > > ``` > > 5.4 在fixture中, 可以把通用的构造条件写成createXXXX()函数,期望的条件exceptXXXX()函数 > > 5.5 一个xxxxunittest.cpp 对应一个xxxx.cpp scr文件 5.6 xxxx.cpp 对应的xxxxMock.h需要放到Mock文件夹中 5.6更多的规范可以参考: [https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/docs/advanced.md](https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/docs/advanced.md) # 5.Other topic solution 1. 抛异常的代码怎么处理 2. 无法使用Mock的场景 2.1 如何跑全局的函数,无法mock只能构造真实对象调用其真实代码 2.2 宏函数,无法mock只能构造真实对象调用其真实代码 2.3 非Virtual public函数 创建真实对象去调用/改为virtual/函数打桩/使用虚函数封装/使用template 静态多态 最后修改:2025 年 07 月 14 日 © 允许规范转载 打赏 赞赏作者 支付宝微信 赞 如果觉得我的文章对你有用,请随意赞赏